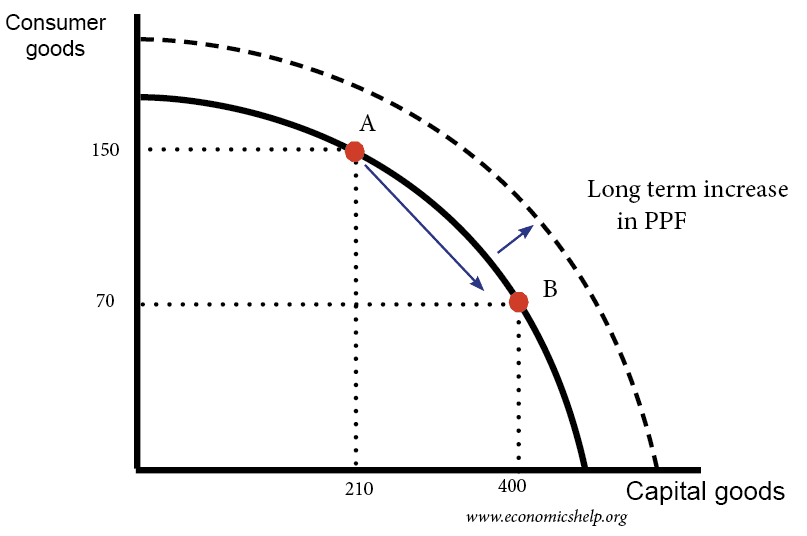
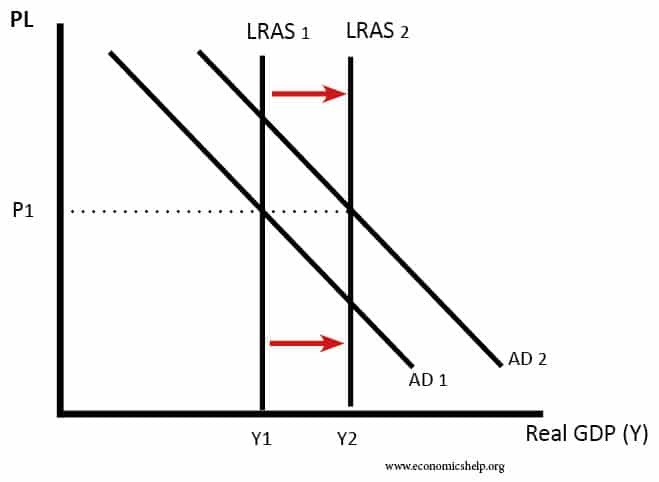
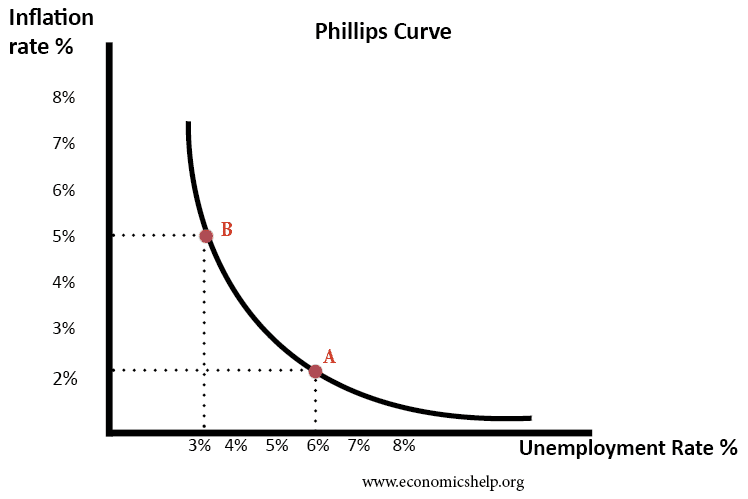
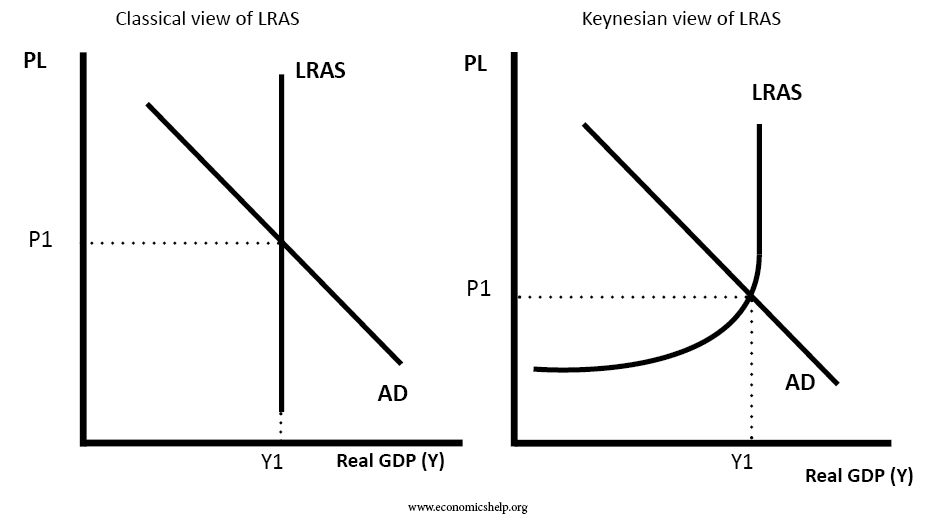
Conflict between economic growth and inflation
Readers Question: What is the relationship between inflation & economic growth? If economic growth is caused by aggregate demand (AD) increasing faster than productive capacity (LRAS) – if economic growth is above the ‘long-run trend rate‘ then economic growth is likely to cause inflation. If economic growth is caused by increased productivity (LRAS), then the …